Causes, Impacts
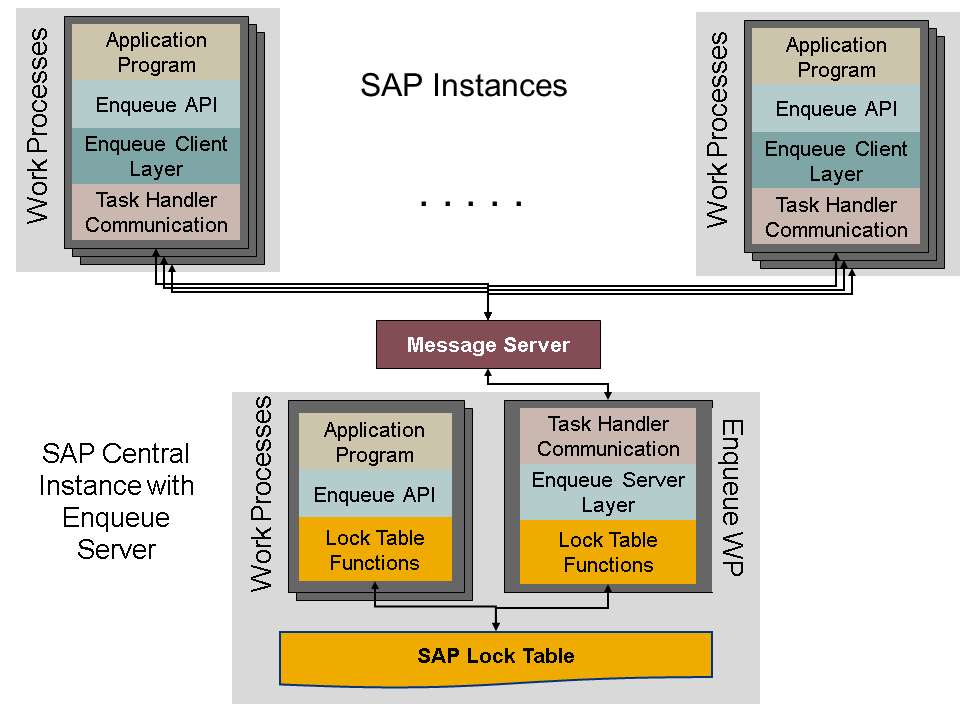
- SAP enqueue server administers the lock table by checking if requested locks do not conflict with existing locks before a new lock can be set and entered in the lock table.
- Some important lock types in SAP that should be taken into consideration include the following:
- Exclusive: Exclusive lock on a database object is only available to and can only be modified by the transaction that set the lock. Subsequently requested exclusive or shared locks on the same object are not permitted. The exclusive lock is released at the end of the transaction or by the respective user as long as the database object has not been changed.
- Exclusive but not cumulative: these locks can only be called once from the same transaction and subsequently requested locks by the same transaction will not be permitted.
- Unduly held locks can be detrimental to SAP system performance, as they can prevent other users from updating critical transactions on the system. The effect of such a problem can be avoided if the enqueue locks and general health condition of the systems are closely monitored.
- Failure to obtain a lock in SAP can result in the termination of important processes on the system which can severely impact business activities.
- Lock resources are a finite queue and thus the limits need to be monitored and managed accordingly. These translates to services managed by the SAP ASCS/SCS/ERS (Central Services) which includes enqueue and enqueue replication to ensure highly available lock management.
How is it monitored?
- Lock operations can be monitored in SAP using SM12 in-built features such as the Enqueue statistics and Top capacity usage.
- SAP Enqueue Resources can be monitored through the CCMS Infrastructure using specific monitoring functions and configuration like the MTEs of transaction RZ20.
- At OS layer: <sid>adm can monitor enqueue and replication using ensmon utility.
For the main topic;
SAP BASIS and Monitoring